
AI Engineering
 |
Description
Book Introduction
Leading AI expert Chip Huyen brings field experience and expertise from NVIDIA, Snorkel AI, and Stanford!
Beyond Model Utilization: A Practical Guide to AI Service Design
“What is a design that is suitable for the product level?”
We've entered an era where anyone can easily create AI applications using the Foundation model.
But when it comes to building real-world, production-level systems, simply making API calls or writing prompts isn't enough.
To transform ideas into user-satisfying services, AI applications must be designed and operated reliably and effectively amidst rapidly changing model environments and technology stacks, increasing usability potential, and associated risks.
This book is a practical guide to AI engineering that provides clear answers to these industry concerns.
This systematically explains the entire process of connecting AI models to real-world services, from various techniques such as prompt engineering, RAG, fine-tuning, agents, and dataset design to designing evaluation metrics, optimizing infrastructure, and building improvement loops through user feedback.
The Foundation Model goes beyond simply explaining "how to use it," and guides you through what problems it can solve and how to design and develop them.
I recommend this book to anyone considering moving beyond foundational models to designing, operating, and improving trusted AI products.
Beyond Model Utilization: A Practical Guide to AI Service Design
“What is a design that is suitable for the product level?”
We've entered an era where anyone can easily create AI applications using the Foundation model.
But when it comes to building real-world, production-level systems, simply making API calls or writing prompts isn't enough.
To transform ideas into user-satisfying services, AI applications must be designed and operated reliably and effectively amidst rapidly changing model environments and technology stacks, increasing usability potential, and associated risks.
This book is a practical guide to AI engineering that provides clear answers to these industry concerns.
This systematically explains the entire process of connecting AI models to real-world services, from various techniques such as prompt engineering, RAG, fine-tuning, agents, and dataset design to designing evaluation metrics, optimizing infrastructure, and building improvement loops through user feedback.
The Foundation Model goes beyond simply explaining "how to use it," and guides you through what problems it can solve and how to design and develop them.
I recommend this book to anyone considering moving beyond foundational models to designing, operating, and improving trusted AI products.
- You can preview some of the book's contents.
Preview
index
Chapter 1: Introduction to AI Applications Using Foundation Models
_1.1 The Rise of AI Engineering
__1.1.1 From Language Models to Large-Scale Language Models
__1.1.2 From large-scale language models to foundation models
__1.1.3 From Foundation Model to AI Engineering
_1.2 Foundation Model Utilization Cases
__1.2.1 Coding
__1.2.2 Image and Video Creation
__1.2.3 Writing
__1.2.4 Education
__1.2.5 Conversational Bot
__1.2.6 Information Aggregation
__1.2.7 Data Systematization
__1.2.8 Workflow Automation
_1.3 AI Application Planning
__1.3.1 Use Case Evaluation
__1.3.2 Setting Expectations
__1.3.3 Milestone Plan
__1.3.4 Maintenance
_1.4 AI Engineering Stack
__1.4.1 Three Layers of AI
__1.4.2 AI Engineering vs. ML Engineering
__1.4.3 AI Engineering vs. Full-Stack Engineering
_1.5 In conclusion
Chapter 2: Understanding the Foundation Model
_2.1 Training data
__2.1.1 Multilingual Model
__2.1.2 Domain-Specific Model
_2.2 Modeling
__2.2.1 Model Architecture
__2.2.2 Model size
_2.3 Post-study
__2.3.1 Map Fine Tuning
__2.3.2 Preference Fine Tuning
_2.4 Sampling
__2.4.1 Sampling Basics
__2.4.2 Sampling Strategy
__2.4.3 Test-point operations
__2.4.4 Structured Output
__2.4.5 Probabilistic Characteristics of AI
_2.5 In conclusion
Chapter 3 Evaluation Methodology
_3.1 Difficulties in Evaluating Foundation Models
_3.2 Understanding Language Modeling Metrics
__3.2.1 Entropy
__3.2.2 Cross entropy
__3.2.3 Bits per character and bits per byte
__3.2.4 Perplexity
__3.2.5 Perplexity Analysis and Application Examples
_3.3 Accurate assessment
__3.3.1 Functional Correctness
__3.3.2 Measuring Reference Data Similarity
__3.3.3 Introduction to Embedding
_3.4 AI Evaluator
__3.4.1 Why Use AI Evaluators?
__3.4.2 How to Use AI Evaluator
__3.4.3 Limitations of AI Evaluators
__3.4.4 Models that can be used as evaluators
_3.5 Ranking models through comparative evaluation
__3.5.1 Tasks of comparative evaluation
__3.5.2 The Future of Comparative Evaluation
_3.6 In conclusion
Chapter 4: Evaluating AI Systems
_4.1 Evaluation Criteria
__4.1.1 Domain-Specific Abilities
__4.1.2 Creation Ability
__4.1.3 Ability to follow instructions
__4.1.4 Cost and Latency
_4.2 Model Selection
__4.2.1 Model Selection Process
__4.2.2 Developing Your Own Model vs. Purchasing a Commercial Model
__4.2.3 Exploring Public Benchmarks
_4.3 Designing the Evaluation Pipeline
__4.3.1 Step 1: Evaluate all components of the system
__4.3.2 Step 2: Creating Evaluation Guidelines
__4.3.3 Step 3: Defining Evaluation Methods and Data
_4.4 In conclusion
Chapter 5: Prompt Engineering
_5.1 Introducing Prompts
__5.1.1 In-Context Learning: Zero-Shot and Few-Shot
__5.1.2 System prompts and user prompts
__5.1.3 Context Length and Context Efficiency
_5.2 Prompt Engineering Best Practices
__5.2.1 Writing Clear and Explicit Instructions
__5.2.2 Providing sufficient context
__5.2.3 Breaking complex tasks into simpler subtasks
__5.2.4 Give the model time to think
__5.2.5 Repeating and Improving Prompts
__5.2.6 Evaluating Prompt Engineering Tools
__5.2.7 Prompt organization and version management
_5.3 Defensive Prompt Engineering
__5.3.1 Engineering Exclusive Prompts and Reverse Prompts
__5.3.2 Jailbreak and Prompt Injection
__5.3.3 Information Extraction
__5.3.4 Defense against prompt attacks
_5.4 In conclusion
Chapter 6 RAG and Agents
_6.1 RAG
__6.1.1 RAG Architecture
__6.1.2 Search Algorithm
__6.1.3 Search Engine Optimization
__6.1.4 RAG Beyond Text
_6.2 Agent
__6.2.1 Agent Overview
__6.2.2 Tools
__6.2.3 Planning
__6.2.4 Agent Failure Types and Evaluation
_6.3 Memory
_6.4 In conclusion
Chapter 7 Fine Tuning
_7.1 Fine Tuning Overview
_7.2 When fine tuning is needed
__7.2.1 Why you should do fine tuning
__7.2.2 Why you shouldn't fine-tune
__7.2.3 Fine Tuning and RAG
_7.3 Memory Bottleneck
__7.3.1 Backpropagation and Learnable Parameters
__7.3.2 Memory calculations
__7.3.3 Numerical representation
__7.3.4 Quantization
_7.4 Fine Tuning Techniques
__7.4.1 Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
__7.4.2 Model Merging and Multi-Task Fine-Tuning
__7.4.3 Fine-tuning tactics
_7.5 In conclusion
Chapter 8 Dataset Engineering
_8.1 Data Curation
__8.1.1 Data Quality
__8.1.2 Data Coverage
__8.1.3 Data volume
__8.1.4 Data Collection and Annotation
_8.2 Data Augmentation and Synthesis
__8.2.1 Why do data synthesis?
__8.2.2 Traditional data generation techniques
__8.2.3 AI-based data synthesis
__8.2.4 Model Distillation
_8.3 Data Processing
__8.3.1 Data Inspection
__8.3.2 Data Deduplication
__8.3.3 Data Cleaning and Filtering
__8.3.4 Matching data formats
_8.4 In conclusion
Chapter 9 Inference Optimization
_9.1 Understanding Inference Optimization
__9.1.1 Inference Overview
__9.1.2 Inference Performance Metrics
__9.1.3 AI Accelerator
_9.2 Inference Optimization
__9.2.1 Model Optimization
__9.2.2 Inference Service Optimization
_9.3 In conclusion
Chapter 10: AI Engineering Architecture and User Feedback
_10.1 AI Engineering Architecture
__10.1.1 Step 1: Context Enrichment
__10.1.2 Step 2: Introducing Guardrails
__10.1.3 Step 3: Adding a Model Router and Gateway
__10.1.4 Step 4: Reducing Latency with Caches
__10.1.5 Step 5: Adding the Agent Pattern
__10.1.6 Monitoring and Observability
__10.1.7 AI Pipeline Orchestration
_10.2 User Feedback
__10.2.1 Extracting Interactive Feedback
__10.2.2 Feedback Design
__10.2.3 Limitations of Feedback
_10.3 In conclusion
_1.1 The Rise of AI Engineering
__1.1.1 From Language Models to Large-Scale Language Models
__1.1.2 From large-scale language models to foundation models
__1.1.3 From Foundation Model to AI Engineering
_1.2 Foundation Model Utilization Cases
__1.2.1 Coding
__1.2.2 Image and Video Creation
__1.2.3 Writing
__1.2.4 Education
__1.2.5 Conversational Bot
__1.2.6 Information Aggregation
__1.2.7 Data Systematization
__1.2.8 Workflow Automation
_1.3 AI Application Planning
__1.3.1 Use Case Evaluation
__1.3.2 Setting Expectations
__1.3.3 Milestone Plan
__1.3.4 Maintenance
_1.4 AI Engineering Stack
__1.4.1 Three Layers of AI
__1.4.2 AI Engineering vs. ML Engineering
__1.4.3 AI Engineering vs. Full-Stack Engineering
_1.5 In conclusion
Chapter 2: Understanding the Foundation Model
_2.1 Training data
__2.1.1 Multilingual Model
__2.1.2 Domain-Specific Model
_2.2 Modeling
__2.2.1 Model Architecture
__2.2.2 Model size
_2.3 Post-study
__2.3.1 Map Fine Tuning
__2.3.2 Preference Fine Tuning
_2.4 Sampling
__2.4.1 Sampling Basics
__2.4.2 Sampling Strategy
__2.4.3 Test-point operations
__2.4.4 Structured Output
__2.4.5 Probabilistic Characteristics of AI
_2.5 In conclusion
Chapter 3 Evaluation Methodology
_3.1 Difficulties in Evaluating Foundation Models
_3.2 Understanding Language Modeling Metrics
__3.2.1 Entropy
__3.2.2 Cross entropy
__3.2.3 Bits per character and bits per byte
__3.2.4 Perplexity
__3.2.5 Perplexity Analysis and Application Examples
_3.3 Accurate assessment
__3.3.1 Functional Correctness
__3.3.2 Measuring Reference Data Similarity
__3.3.3 Introduction to Embedding
_3.4 AI Evaluator
__3.4.1 Why Use AI Evaluators?
__3.4.2 How to Use AI Evaluator
__3.4.3 Limitations of AI Evaluators
__3.4.4 Models that can be used as evaluators
_3.5 Ranking models through comparative evaluation
__3.5.1 Tasks of comparative evaluation
__3.5.2 The Future of Comparative Evaluation
_3.6 In conclusion
Chapter 4: Evaluating AI Systems
_4.1 Evaluation Criteria
__4.1.1 Domain-Specific Abilities
__4.1.2 Creation Ability
__4.1.3 Ability to follow instructions
__4.1.4 Cost and Latency
_4.2 Model Selection
__4.2.1 Model Selection Process
__4.2.2 Developing Your Own Model vs. Purchasing a Commercial Model
__4.2.3 Exploring Public Benchmarks
_4.3 Designing the Evaluation Pipeline
__4.3.1 Step 1: Evaluate all components of the system
__4.3.2 Step 2: Creating Evaluation Guidelines
__4.3.3 Step 3: Defining Evaluation Methods and Data
_4.4 In conclusion
Chapter 5: Prompt Engineering
_5.1 Introducing Prompts
__5.1.1 In-Context Learning: Zero-Shot and Few-Shot
__5.1.2 System prompts and user prompts
__5.1.3 Context Length and Context Efficiency
_5.2 Prompt Engineering Best Practices
__5.2.1 Writing Clear and Explicit Instructions
__5.2.2 Providing sufficient context
__5.2.3 Breaking complex tasks into simpler subtasks
__5.2.4 Give the model time to think
__5.2.5 Repeating and Improving Prompts
__5.2.6 Evaluating Prompt Engineering Tools
__5.2.7 Prompt organization and version management
_5.3 Defensive Prompt Engineering
__5.3.1 Engineering Exclusive Prompts and Reverse Prompts
__5.3.2 Jailbreak and Prompt Injection
__5.3.3 Information Extraction
__5.3.4 Defense against prompt attacks
_5.4 In conclusion
Chapter 6 RAG and Agents
_6.1 RAG
__6.1.1 RAG Architecture
__6.1.2 Search Algorithm
__6.1.3 Search Engine Optimization
__6.1.4 RAG Beyond Text
_6.2 Agent
__6.2.1 Agent Overview
__6.2.2 Tools
__6.2.3 Planning
__6.2.4 Agent Failure Types and Evaluation
_6.3 Memory
_6.4 In conclusion
Chapter 7 Fine Tuning
_7.1 Fine Tuning Overview
_7.2 When fine tuning is needed
__7.2.1 Why you should do fine tuning
__7.2.2 Why you shouldn't fine-tune
__7.2.3 Fine Tuning and RAG
_7.3 Memory Bottleneck
__7.3.1 Backpropagation and Learnable Parameters
__7.3.2 Memory calculations
__7.3.3 Numerical representation
__7.3.4 Quantization
_7.4 Fine Tuning Techniques
__7.4.1 Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
__7.4.2 Model Merging and Multi-Task Fine-Tuning
__7.4.3 Fine-tuning tactics
_7.5 In conclusion
Chapter 8 Dataset Engineering
_8.1 Data Curation
__8.1.1 Data Quality
__8.1.2 Data Coverage
__8.1.3 Data volume
__8.1.4 Data Collection and Annotation
_8.2 Data Augmentation and Synthesis
__8.2.1 Why do data synthesis?
__8.2.2 Traditional data generation techniques
__8.2.3 AI-based data synthesis
__8.2.4 Model Distillation
_8.3 Data Processing
__8.3.1 Data Inspection
__8.3.2 Data Deduplication
__8.3.3 Data Cleaning and Filtering
__8.3.4 Matching data formats
_8.4 In conclusion
Chapter 9 Inference Optimization
_9.1 Understanding Inference Optimization
__9.1.1 Inference Overview
__9.1.2 Inference Performance Metrics
__9.1.3 AI Accelerator
_9.2 Inference Optimization
__9.2.1 Model Optimization
__9.2.2 Inference Service Optimization
_9.3 In conclusion
Chapter 10: AI Engineering Architecture and User Feedback
_10.1 AI Engineering Architecture
__10.1.1 Step 1: Context Enrichment
__10.1.2 Step 2: Introducing Guardrails
__10.1.3 Step 3: Adding a Model Router and Gateway
__10.1.4 Step 4: Reducing Latency with Caches
__10.1.5 Step 5: Adding the Agent Pattern
__10.1.6 Monitoring and Observability
__10.1.7 AI Pipeline Orchestration
_10.2 User Feedback
__10.2.1 Extracting Interactive Feedback
__10.2.2 Feedback Design
__10.2.3 Limitations of Feedback
_10.3 In conclusion
Detailed image
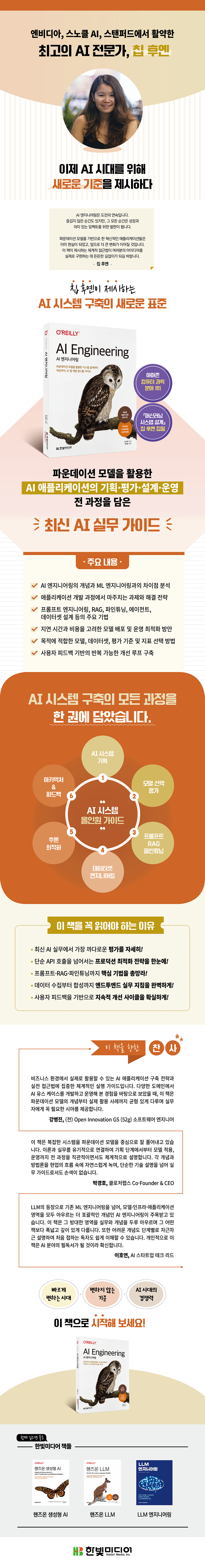
Publisher's Review
From AI system planning to design and operation, bridging the gap between theory and reality
A new standard that captures the essence of AI engineering in a realistic and efficient way.
While prototyping an idea has become easier, turning it into a reliable AI product is a completely different story.
Fragmented knowledge scattered across the web and generative AI alone is insufficient to address the challenges faced in complex production environments.
"AI Engineering" begins at this very point, providing a cutting-edge practical guide covering the entire process of planning, designing, and operating AI applications utilizing the Foundation Model. Rather than presenting abstract theory, it presents a systematic framework that bridges the gaps in the field.
This book organically connects and explains the essential knowledge for practitioners, from prompt engineering, RAG, fine-tuning, inference optimization, and architecture design.
Rather than simply listing technologies, it addresses the challenges and decision-making context faced by actual teams, providing a balanced view of technology and the realities of the field.
It's a structure that provides both practical insights that can be applied immediately in the field and the principles necessary for long-term growth.
What makes this book stand out most is that it treats evaluation as a core topic, not just an appendix. Because the quality and reliability of AI systems cannot be guaranteed without evaluation, two chapters focus on evaluation methodologies that ensure performance and reliability.
This will enable you to establish decision-making principles based on data, not just "feelings." Like its predecessor, "Machine Learning System Design," this book will serve as a solid textbook and reference, laying the foundation for a foundation that will remain unshaken even in the rapidly changing AI ecosystem.
● Present clear concepts and roadmap: Define how AI engineering differs from traditional ML engineering and provide a holistic view and strategy for developing successful AI applications.
● Core strategies to maximize performance and efficiency: Goes beyond simply listing the latest techniques like prompt engineering, RAG, and fine-tuning, and presents clear criteria and trade-offs for when to use what.
● Strengthening data-driven decision-making capabilities: We provide a systematic evaluation pipeline design method and practical indicator selection guide to help you select the optimal combination of models and technologies to drive project success among numerous models and technologies.
● Practical Operational Know-How: Learn practical optimization methods for deploying and operating AI systems within realistic constraints such as latency and cost.
● Building a sustainable system: Learn how to systematically collect and reflect user feedback to create an AI system that is continuously improved, rather than just built once.
Key Contents
● Analysis of the concept of AI engineering and its differences from ML engineering
● Challenges encountered during application development and solution strategies
● Key techniques such as prompt engineering, RAG, fine-tuning, agents, and dataset design
● Optimization of model deployment and operation considering delay time and cost
● How to select models, datasets, evaluation criteria, and indicators appropriate for the purpose
● Build a repeatable improvement loop based on user feedback
Who is this book for?
● AI/ML engineers who want to implement or expand the LLM and foundation models into their practice
● Data scientists and researchers who want to apply model evaluation, dataset design, and fine-tuning techniques to real-world projects.
● Product managers and planners who need to understand the AI application development process and collaborate with the team
● ML developers facing new challenges as they transition from traditional ML to LLM-based development
A new standard that captures the essence of AI engineering in a realistic and efficient way.
While prototyping an idea has become easier, turning it into a reliable AI product is a completely different story.
Fragmented knowledge scattered across the web and generative AI alone is insufficient to address the challenges faced in complex production environments.
"AI Engineering" begins at this very point, providing a cutting-edge practical guide covering the entire process of planning, designing, and operating AI applications utilizing the Foundation Model. Rather than presenting abstract theory, it presents a systematic framework that bridges the gaps in the field.
This book organically connects and explains the essential knowledge for practitioners, from prompt engineering, RAG, fine-tuning, inference optimization, and architecture design.
Rather than simply listing technologies, it addresses the challenges and decision-making context faced by actual teams, providing a balanced view of technology and the realities of the field.
It's a structure that provides both practical insights that can be applied immediately in the field and the principles necessary for long-term growth.
What makes this book stand out most is that it treats evaluation as a core topic, not just an appendix. Because the quality and reliability of AI systems cannot be guaranteed without evaluation, two chapters focus on evaluation methodologies that ensure performance and reliability.
This will enable you to establish decision-making principles based on data, not just "feelings." Like its predecessor, "Machine Learning System Design," this book will serve as a solid textbook and reference, laying the foundation for a foundation that will remain unshaken even in the rapidly changing AI ecosystem.
● Present clear concepts and roadmap: Define how AI engineering differs from traditional ML engineering and provide a holistic view and strategy for developing successful AI applications.
● Core strategies to maximize performance and efficiency: Goes beyond simply listing the latest techniques like prompt engineering, RAG, and fine-tuning, and presents clear criteria and trade-offs for when to use what.
● Strengthening data-driven decision-making capabilities: We provide a systematic evaluation pipeline design method and practical indicator selection guide to help you select the optimal combination of models and technologies to drive project success among numerous models and technologies.
● Practical Operational Know-How: Learn practical optimization methods for deploying and operating AI systems within realistic constraints such as latency and cost.
● Building a sustainable system: Learn how to systematically collect and reflect user feedback to create an AI system that is continuously improved, rather than just built once.
Key Contents
● Analysis of the concept of AI engineering and its differences from ML engineering
● Challenges encountered during application development and solution strategies
● Key techniques such as prompt engineering, RAG, fine-tuning, agents, and dataset design
● Optimization of model deployment and operation considering delay time and cost
● How to select models, datasets, evaluation criteria, and indicators appropriate for the purpose
● Build a repeatable improvement loop based on user feedback
Who is this book for?
● AI/ML engineers who want to implement or expand the LLM and foundation models into their practice
● Data scientists and researchers who want to apply model evaluation, dataset design, and fine-tuning techniques to real-world projects.
● Product managers and planners who need to understand the AI application development process and collaborate with the team
● ML developers facing new challenges as they transition from traditional ML to LLM-based development
GOODS SPECIFICS
- Date of issue: September 30, 2025
- Page count, weight, size: 580 pages | 183*235*35mm
- ISBN13: 9791169214278
- ISBN10: 1169214274
You may also like
카테고리
korean


korean


![ELLE 엘르 A형 (여성월간) : 1월 [2026]](http://librairie.coreenne.fr/cdn/shop/files/3b70e1cf77cf67d6da56e0eb041901e8.jpg?v=1767265322&width=3840)























