
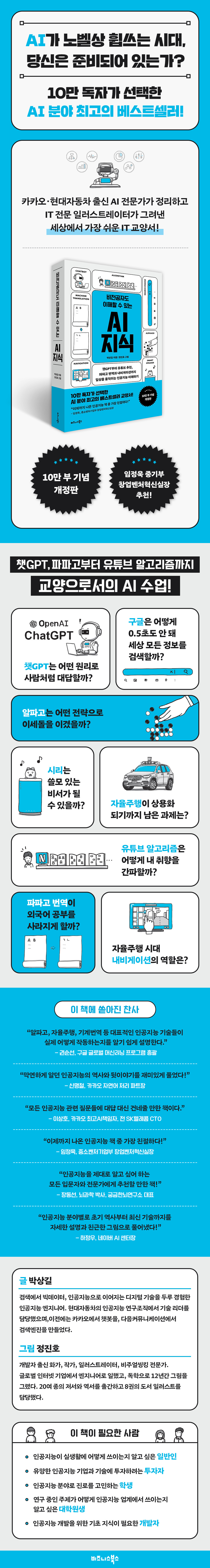
AI knowledge that even non-specialists can understand
 |
Description
Book Introduction
Chosen by 100,000 readers The best-selling textbook in the AI field! “This is the most friendly AI book ever published!” Lim Jeong-wook, Director of the Startup and Venture Innovation Office, Ministry of SMEs and Startups The most useful AI textbook chosen by readers, a revised edition commemorating the 100,000th copy sale! The reality and future of artificial intelligence as seen by a current AI expert! First published in 2022, "AI Knowledge Even Non-Majors Can Understand," which has consistently enjoyed the love of over 100,000 readers and established itself as a popular AI textbook, has published a revised edition that reflects the latest AI technology trends. Not only has the content on ChatGPT, which became a hot topic with the release of GPT-4 in 2023, been significantly supplemented, but the parts that have changed as of 2024 have been comprehensively updated. New smartphones are breaking down language barriers by offering real-time translation, and AI is increasingly being incorporated into existing devices and software, such as KakaoTalk, which summarizes conversations. And now, AI-synthesized images are becoming so realistic that they are difficult to distinguish from reality, and they are frequently appearing on our timelines. AI technology is now personalized and popular, and is already integrating into every aspect of our lives. The author is an expert in AI technology, having created a chatbot at Kakao, a search engine at Daum, and served as the leader of the AI team at Hyundai Motor Company. Based on these experiences, the author tells us the most useful stories about AI, not abstract stories surrounding it, but stories that are actually changing reality. Additionally, over 300 pictures are provided to aid understanding instead of difficult formulas. Author Jin-ho Jeong, who started out as a developer and later became an IT professional illustrator, explains AI principles in simple drawings so that anyone can easily understand them. Nowadays, it is difficult to conduct daily conversations or even work without knowing about AI. This book details eight representative uses of AI, and goes beyond that to explain the specific principles of how each service works in a way that even non-experts can easily understand. This will broaden your understanding of technology and science, teach you how to effectively utilize it in your work and daily life, and help you apply it widely in other fields. Everyone, from the general public who wants to understand what AI is and how it's used in real-life situations, to technology investors, those considering a career in AI, and even developers seeking foundational knowledge for AI development, will gain insight into the utility of AI. |
- You can preview some of the book's contents.
Preview
index
Recommendation
Publishing a revised edition commemorating the 100,000th copy release
Entering
Chapter 1.
Artificial Intelligence | Great AI, Awakening
The first chess machine to beat humans 250 years ago
True artificial intelligence emerges
Rule-based, AI-enabled implementation
Machine learning, discovering rules on its own
The Emergence of Deep Learning, a Core Technology in AI
Data, the crude oil of artificial intelligence
Systems, GPUs Perfect AI
Open source, innovation where everyone participates
Great AI Awakens
Chapter 2.
AlphaGo | The Emergence of a Machine That Surpasses Humans
How did Deep Blue become a chess champion?
Baduk, can you calculate all the necessary moves?
Lee Sedol, the genius player representing humanity
Monte Carlo method using the probability of gambling
Policy Network: Where to Put the Stones?
Value network, judging the situation
How AlphaGo plays
A stroke of genius
AlphaGo Zero: No Human Needed
AlphaZero, Towards True Artificial Intelligence
Chapter 3.
Autonomous Driving | Tesla's Dream Machine
The DARPA Grand Challenge: The Beginning of Autonomous Driving
What's the secret behind Stanley's self-driving car victory?
The formula for autonomous driving: Bayes' theorem
Sensor Wars: Radar, Lidar, and Cameras
Cameras, looking at the road through the eyes of animals
Imitation learning: mimicking human driving habits
Is fully autonomous driving possible?
The Autonomous Driving Dilemma: Who Should Be Sacrifice?
The future that self-driving cars will change
Chapter 4.
Search Engine | How Google Searches the World
Search engines emerge
Make a lot of money
Collect a huge amount of documents
How do search engines search?
Ranking, a technology worth trillions of dollars
Find the latest documents
Finding quality documents
PageRank: The Birth of Google's History
How to find documents that perfectly match your query
TF-IDF and the magical BM25
A/B Testing: How to Improve Search
Search Engine Optimization: A Battle of Spears and Shields
The Evolution of Google Search: Its Smarter Evolution
Chapter 5.
Smart Speaker | Can Siri Become a Useful Assistant?
The Birth of an AI Assistant
Apple's Siri ushered in the era of voice assistants.
Amazon Alexa Usheres in the Era of Smart Speakers
How do smart speakers understand speech?
Voice recognition process that recognizes human voices
Acoustic models recognize words from speech waveforms.
Language models correct misrecognized words
Natural Language Understanding, Understanding Language
Dialog Manager, execute commands
Natural Language Generation, Designing Conversations
Connective Synthesis: Can Sentences Be Read Naturally?
Voice synthesis: Towards more naturalness than humans
Chapter 6.
Machine Translation | Even if you don't know a foreign language, you can use Papago.
Great AI Awakens
Why Human Language Is So Difficult
The Beginning of Machine Translation
Rule-based, define all the rules
Example-based and statistical-based, demonstrating possibilities
Artificial Neural Networks: Innovation Finally Begins
Attention, the most revolutionary invention
Learn the translation rules yourself
Machine translation surpasses human capabilities
The Tower of Babel: Can humans overcome God's punishment?
Chapter 7.
Chatbot | ChatGPT, Create a Report in Under a Minute
Why did the chatbot Iruda stop service after just two weeks?
Compilers: Computers Understand Human Language
The emergence of Kakao Bank's customer center chatbot
Convert coordinates and geometry into numbers
Word2Vec, turning language into numbers
Find similar words using cosine distance
Can we communicate freely with machines?
How machines generate sentences
GPT-3, a language generation model that outperforms humans
Chatbots from Google and Facebook are on the rise.
ChatGPT, the King of Chatbots
GPT-4: Finally Approaching the Era of True Artificial Intelligence
Can machines understand language?
Turing Test and Chinese Room
AI Asks for True Understanding
Chapter 8.
Navigation | How does T Map find the fastest route?
Navigation, your smart driving assistant
Occam's Razor
Data that influences predictions
Decision Trees: The Power of Simple Models
Random Forests: Harnessing the Wisdom of the Crowd
Gradient Boosting: Reducing the Distance from the Correct Answer
Dijkstra's Algorithm: The Secret to Finding the Shortest Path
The A* algorithm adopted by all navigation systems
More than just navigation and route guidance
Chapter 9.
Recommendation Algorithm | The Mysterious YouTube Algorithm Led You Here
Recommendation services, from Netflix to YouTube
Beer and diapers are sold together.
An algorithm that predicted pregnancy in teenage girls
The Beginning of a Recommendation System
Collaborative filtering: recommending similar customers
Factorizing matrices: A magical algorithm for finding latent factors
YouTube recommendation algorithm using deep learning
Glossary
Americas
Publishing a revised edition commemorating the 100,000th copy release
Entering
Chapter 1.
Artificial Intelligence | Great AI, Awakening
The first chess machine to beat humans 250 years ago
True artificial intelligence emerges
Rule-based, AI-enabled implementation
Machine learning, discovering rules on its own
The Emergence of Deep Learning, a Core Technology in AI
Data, the crude oil of artificial intelligence
Systems, GPUs Perfect AI
Open source, innovation where everyone participates
Great AI Awakens
Chapter 2.
AlphaGo | The Emergence of a Machine That Surpasses Humans
How did Deep Blue become a chess champion?
Baduk, can you calculate all the necessary moves?
Lee Sedol, the genius player representing humanity
Monte Carlo method using the probability of gambling
Policy Network: Where to Put the Stones?
Value network, judging the situation
How AlphaGo plays
A stroke of genius
AlphaGo Zero: No Human Needed
AlphaZero, Towards True Artificial Intelligence
Chapter 3.
Autonomous Driving | Tesla's Dream Machine
The DARPA Grand Challenge: The Beginning of Autonomous Driving
What's the secret behind Stanley's self-driving car victory?
The formula for autonomous driving: Bayes' theorem
Sensor Wars: Radar, Lidar, and Cameras
Cameras, looking at the road through the eyes of animals
Imitation learning: mimicking human driving habits
Is fully autonomous driving possible?
The Autonomous Driving Dilemma: Who Should Be Sacrifice?
The future that self-driving cars will change
Chapter 4.
Search Engine | How Google Searches the World
Search engines emerge
Make a lot of money
Collect a huge amount of documents
How do search engines search?
Ranking, a technology worth trillions of dollars
Find the latest documents
Finding quality documents
PageRank: The Birth of Google's History
How to find documents that perfectly match your query
TF-IDF and the magical BM25
A/B Testing: How to Improve Search
Search Engine Optimization: A Battle of Spears and Shields
The Evolution of Google Search: Its Smarter Evolution
Chapter 5.
Smart Speaker | Can Siri Become a Useful Assistant?
The Birth of an AI Assistant
Apple's Siri ushered in the era of voice assistants.
Amazon Alexa Usheres in the Era of Smart Speakers
How do smart speakers understand speech?
Voice recognition process that recognizes human voices
Acoustic models recognize words from speech waveforms.
Language models correct misrecognized words
Natural Language Understanding, Understanding Language
Dialog Manager, execute commands
Natural Language Generation, Designing Conversations
Connective Synthesis: Can Sentences Be Read Naturally?
Voice synthesis: Towards more naturalness than humans
Chapter 6.
Machine Translation | Even if you don't know a foreign language, you can use Papago.
Great AI Awakens
Why Human Language Is So Difficult
The Beginning of Machine Translation
Rule-based, define all the rules
Example-based and statistical-based, demonstrating possibilities
Artificial Neural Networks: Innovation Finally Begins
Attention, the most revolutionary invention
Learn the translation rules yourself
Machine translation surpasses human capabilities
The Tower of Babel: Can humans overcome God's punishment?
Chapter 7.
Chatbot | ChatGPT, Create a Report in Under a Minute
Why did the chatbot Iruda stop service after just two weeks?
Compilers: Computers Understand Human Language
The emergence of Kakao Bank's customer center chatbot
Convert coordinates and geometry into numbers
Word2Vec, turning language into numbers
Find similar words using cosine distance
Can we communicate freely with machines?
How machines generate sentences
GPT-3, a language generation model that outperforms humans
Chatbots from Google and Facebook are on the rise.
ChatGPT, the King of Chatbots
GPT-4: Finally Approaching the Era of True Artificial Intelligence
Can machines understand language?
Turing Test and Chinese Room
AI Asks for True Understanding
Chapter 8.
Navigation | How does T Map find the fastest route?
Navigation, your smart driving assistant
Occam's Razor
Data that influences predictions
Decision Trees: The Power of Simple Models
Random Forests: Harnessing the Wisdom of the Crowd
Gradient Boosting: Reducing the Distance from the Correct Answer
Dijkstra's Algorithm: The Secret to Finding the Shortest Path
The A* algorithm adopted by all navigation systems
More than just navigation and route guidance
Chapter 9.
Recommendation Algorithm | The Mysterious YouTube Algorithm Led You Here
Recommendation services, from Netflix to YouTube
Beer and diapers are sold together.
An algorithm that predicted pregnancy in teenage girls
The Beginning of a Recommendation System
Collaborative filtering: recommending similar customers
Factorizing matrices: A magical algorithm for finding latent factors
YouTube recommendation algorithm using deep learning
Glossary
Americas
Detailed image
Into the book
What is artificial intelligence? Alan Turing posed the bold question, "Can machines think?" and proposed that, rather than defining "thinking," we should consider something to be "thinking" if it can satisfactorily simulate the act of thinking.
This is the 'Imitation Game', the name given by Alan Turing in his paper and also famously used as the title of a movie.
I, too, would like to answer the question, "What is artificial intelligence?" in the same way.
Instead of defining artificial intelligence like Turing, if we can satisfactorily prove the usefulness of artificial intelligence, then we can consider ourselves to have “understood artificial intelligence.”
So, I want to introduce you to the usefulness of artificial intelligence.
--- From "Entering"
In 1770, a novel chess machine appeared in Austria.
It was an automaton playing chess, with a carved doll wearing Ottoman costume and a turban on its head sitting behind a chessboard.
The surprising thing was that this machine played chess by itself.
Moreover, his skills were so outstanding that he could beat most people.
Naturally, many people suspected that there was a person hiding inside the machine.
Suspicious people looked into every nook and cranny of the machine, but found nothing but a mechanical device consisting of unknown levers and springs.
…what on earth was the identity of this chess-playing automaton?
--- From "Artificial Intelligence│Great Artificial Intelligence, Awakening"
Tesla recorded its first fatal accident in Florida in May 2016, just seven months after launching its self-driving feature.
It was an accident where a white trailer was hit from the side.
At the time, the Tesla Model S did not recognize the side of the white trailer as an obstacle at all and ended up ramming it without slowing down.
The vehicle was mangled and the driver died on the spot.
According to a later accident report, the driver was behind the wheel for only 25 seconds during the 37 minutes.
Not only that, the warning sound to keep your hands on the steering wheel sounded seven times.
He was overconfident in Tesla's self-driving capabilities.
--- From "Autonomous Driving│Tesla's Dream Machine"
How can search alone generate such enormous revenue? Randomly displaying ads doesn't increase clicks.
The key is to increase the likelihood of clicks.
We needed to display ads that were contextually relevant to the user so they would click on them.
For example, if a man in his 30s working in an office in a large city searches for 'shirts', famous brands such as 'Polo' and 'Beanpole' will be displayed, and further encouraging him to make an online purchase.
…This is the typical search advertising model and search engine revenue model.
It is also Google's representative revenue model.
Google generated $330 billion in advertising revenue this way in 2023 alone.
--- From "Search Engine│How Google Searches the World"
Siri is now under Apple's wing, just two months after its launch.
Plans to release Android and BlackBerry versions were of course canceled, and work is now underway to integrate Siri with the iPhone.
Even after the acquisition, Jobs showed great interest by attending Siri's weekly meetings.
A few months before the product's unveiling, the Siri development team and Jobs ran into each other in the cafeteria. Steve Jobs, who usually greeted everyone else perfunctory, stopped and greeted the Siri team warmly.
“Hey Siri friends! How are things going?”
--- From "Smart Speaker│Can Siri Become a Useful Secretary?"
Let's ask the speaker once, "How's the weather today?"
Will the speaker actually recognize "Fuck, shit" as "Fuck, shit"? Of course, the acoustic model can.
But language models never perceive it this way.
The language model is what we call prior knowledge.
The language model has never seen the sentence 'the weather sucks' before.
So, there is no way that you would have any relevant knowledge.
Clearly, the language model has seen the sentence 'what's the weather' countless times and has prior knowledge.
Therefore, we already know with a high probability that the phrase 'what is the weather like today' will be followed by 'how is it'.
The language model recalibrates the acoustic model based on probabilities even if it misrecognizes the voice.
It's a correction to 'The weather sucks today', which we often ask, 'How's the weather today?'
--- From "Smart Speaker│Can Siri Become a Useful Secretary?"
We no longer input rules into machine translation.
Learn the rules yourself from similar sentences.
It's about solving the complex problem of translation on your own using data.
All you need to improve performance is more data, more sentences.
The rest is all learned by the machine itself.
Neural network-based models are constantly evolving.
Research is becoming more active with the introduction of the concept of attention, which goes beyond simply learning entire sentences and focuses on important words.
Around this time, there was even talk that the research results of the past two years had surpassed those of the previous 20 years.
--- From "Machine Translation│If you don't know a foreign language, just have Papago"
As if to reward the long wait, GPT-4 boasts remarkably superior performance.
It outperforms existing models in many areas.
When I took the bar exam, the existing ChatGPT scored 213 out of 400, which was in the bottom 10%.
However, GPT-4 reached the top 10% with a score of 298.
This is enough to pass the New York State Bar Exam.
He also scored 700 out of 800 on the American SAT Math Test, which is equivalent to Korea's College Scholastic Ability Test.
Likewise, it is a score that is in the top 10%.
It's not just about being good at English.
We tested machine translation of some data in English into Italian, Spanish, German, French, Korean, and Japanese, and the results were significantly higher than those obtained with the existing ChatGPT for processing English sentences.
The new GPT-4's Korean answers are more accurate than the existing ChatGPT's English answers.
--- From "Chatbot│ChatGPT, Write a Report in 1 Minute"
The original recommendation system was actually Amazon.
Since the 1990s, Amazon has achieved significant success by recommending products related to what customers have purchased, products likely to be of interest to them, and ultimately products they are likely to purchase.
…Amazon's recommendation system initially only listed related products, but it has since become a successful service that influences click-through and purchase rates.
The key to recommender systems is that they become more sophisticated the more you use them.
As data grows and information becomes more abundant, more accurate recommendations become possible.
Recommendation systems account for a significant portion of total sales.
They say that 35% of Amazon product sales come from recommendations.
This is the 'Imitation Game', the name given by Alan Turing in his paper and also famously used as the title of a movie.
I, too, would like to answer the question, "What is artificial intelligence?" in the same way.
Instead of defining artificial intelligence like Turing, if we can satisfactorily prove the usefulness of artificial intelligence, then we can consider ourselves to have “understood artificial intelligence.”
So, I want to introduce you to the usefulness of artificial intelligence.
--- From "Entering"
In 1770, a novel chess machine appeared in Austria.
It was an automaton playing chess, with a carved doll wearing Ottoman costume and a turban on its head sitting behind a chessboard.
The surprising thing was that this machine played chess by itself.
Moreover, his skills were so outstanding that he could beat most people.
Naturally, many people suspected that there was a person hiding inside the machine.
Suspicious people looked into every nook and cranny of the machine, but found nothing but a mechanical device consisting of unknown levers and springs.
…what on earth was the identity of this chess-playing automaton?
--- From "Artificial Intelligence│Great Artificial Intelligence, Awakening"
Tesla recorded its first fatal accident in Florida in May 2016, just seven months after launching its self-driving feature.
It was an accident where a white trailer was hit from the side.
At the time, the Tesla Model S did not recognize the side of the white trailer as an obstacle at all and ended up ramming it without slowing down.
The vehicle was mangled and the driver died on the spot.
According to a later accident report, the driver was behind the wheel for only 25 seconds during the 37 minutes.
Not only that, the warning sound to keep your hands on the steering wheel sounded seven times.
He was overconfident in Tesla's self-driving capabilities.
--- From "Autonomous Driving│Tesla's Dream Machine"
How can search alone generate such enormous revenue? Randomly displaying ads doesn't increase clicks.
The key is to increase the likelihood of clicks.
We needed to display ads that were contextually relevant to the user so they would click on them.
For example, if a man in his 30s working in an office in a large city searches for 'shirts', famous brands such as 'Polo' and 'Beanpole' will be displayed, and further encouraging him to make an online purchase.
…This is the typical search advertising model and search engine revenue model.
It is also Google's representative revenue model.
Google generated $330 billion in advertising revenue this way in 2023 alone.
--- From "Search Engine│How Google Searches the World"
Siri is now under Apple's wing, just two months after its launch.
Plans to release Android and BlackBerry versions were of course canceled, and work is now underway to integrate Siri with the iPhone.
Even after the acquisition, Jobs showed great interest by attending Siri's weekly meetings.
A few months before the product's unveiling, the Siri development team and Jobs ran into each other in the cafeteria. Steve Jobs, who usually greeted everyone else perfunctory, stopped and greeted the Siri team warmly.
“Hey Siri friends! How are things going?”
--- From "Smart Speaker│Can Siri Become a Useful Secretary?"
Let's ask the speaker once, "How's the weather today?"
Will the speaker actually recognize "Fuck, shit" as "Fuck, shit"? Of course, the acoustic model can.
But language models never perceive it this way.
The language model is what we call prior knowledge.
The language model has never seen the sentence 'the weather sucks' before.
So, there is no way that you would have any relevant knowledge.
Clearly, the language model has seen the sentence 'what's the weather' countless times and has prior knowledge.
Therefore, we already know with a high probability that the phrase 'what is the weather like today' will be followed by 'how is it'.
The language model recalibrates the acoustic model based on probabilities even if it misrecognizes the voice.
It's a correction to 'The weather sucks today', which we often ask, 'How's the weather today?'
--- From "Smart Speaker│Can Siri Become a Useful Secretary?"
We no longer input rules into machine translation.
Learn the rules yourself from similar sentences.
It's about solving the complex problem of translation on your own using data.
All you need to improve performance is more data, more sentences.
The rest is all learned by the machine itself.
Neural network-based models are constantly evolving.
Research is becoming more active with the introduction of the concept of attention, which goes beyond simply learning entire sentences and focuses on important words.
Around this time, there was even talk that the research results of the past two years had surpassed those of the previous 20 years.
--- From "Machine Translation│If you don't know a foreign language, just have Papago"
As if to reward the long wait, GPT-4 boasts remarkably superior performance.
It outperforms existing models in many areas.
When I took the bar exam, the existing ChatGPT scored 213 out of 400, which was in the bottom 10%.
However, GPT-4 reached the top 10% with a score of 298.
This is enough to pass the New York State Bar Exam.
He also scored 700 out of 800 on the American SAT Math Test, which is equivalent to Korea's College Scholastic Ability Test.
Likewise, it is a score that is in the top 10%.
It's not just about being good at English.
We tested machine translation of some data in English into Italian, Spanish, German, French, Korean, and Japanese, and the results were significantly higher than those obtained with the existing ChatGPT for processing English sentences.
The new GPT-4's Korean answers are more accurate than the existing ChatGPT's English answers.
--- From "Chatbot│ChatGPT, Write a Report in 1 Minute"
The original recommendation system was actually Amazon.
Since the 1990s, Amazon has achieved significant success by recommending products related to what customers have purchased, products likely to be of interest to them, and ultimately products they are likely to purchase.
…Amazon's recommendation system initially only listed related products, but it has since become a successful service that influences click-through and purchase rates.
The key to recommender systems is that they become more sophisticated the more you use them.
As data grows and information becomes more abundant, more accurate recommendations become possible.
Recommendation systems account for a significant portion of total sales.
They say that 35% of Amazon product sales come from recommendations.
--- From "Recommendation Algorithm│The Unknown YouTube Algorithm Led Me Here"
Publisher's Review
An era where AI comprehension becomes competitive!
AI classes as a liberal arts course for survival in the digital age
'I wake up in the morning and ask my smart speaker about the weather.
If I have any questions, I immediately search the portal.
When you go somewhere, you enter the destination into the navigation system.
'I browse through the videos recommended by YouTube or Netflix.' This is a scene from our daily lives.
And all of these scenes are made with AI technology.
As autonomous driving, search engines, smart speakers, machine translation, chatbots, navigation, and recommendation algorithms become part of our daily lives, we may feel that our lives have become more convenient, but innovative AI technologies are at work within them.
This book explains these techniques in language we can understand.
It provides a friendly explanation of the principles of artificial intelligence technology closely related to our daily lives, such as how Google finds the information we need in less than a second, how chatbots provide the right answers, and how recommendation algorithms discover our tastes.
"AI Knowledge Even Non-Majors Can Understand" was written to help diverse people understand AI and utilize it in their fields in this era where AI is a given tool.
This book explains the history and principles of AI technology in a general-level manner, making it easy for those who have never studied the subject before or find science and math difficult to understand.
The author says that AI technology will soon be used in everyday life.
Just as smartphones, which were initially used only by a select group of people, are now used by 95% of adults in our country in less than 10 years.
The author says that sooner or later, only those who know how to integrate and utilize AI in their work—from agriculture and fisheries to office work like accounting and marketing, and even specialized fields like medicine and law—will be able to keep up with the demands of the times.
The ability to leverage AI technology to find solutions at incredible speed from massive amounts of data is itself a competitive edge in business.
The author is an expert in AI technology, having created a chatbot at Kakao, a search engine at Daum, and served as the leader of the AI team at Hyundai Motor Company.
Based on these experiences, the author tells us the most useful story about AI, one that is changing the real world, rather than an abstract story surrounding it.
Additionally, over 300 pictures are provided to aid understanding instead of difficult formulas.
Jin-ho Jeong, a former developer turned IT professional illustrator, explains AI principles in simple drawings that anyone can easily understand.
Even now, AI technology is active in invisible places in our daily lives.
And these uses will only grow.
So what we need now is not fear of AI, but to realize and understand its usefulness.
This book will open new opportunities for those considering how to incorporate AI into their fields of study and work.
From ChatGPT to Google Search, Naver Papago, and YouTube algorithms.
Easily unravel the principles of all the AI technologies that have transformed our daily lives.
Before examining the full utility of artificial intelligence, this book first examines what artificial intelligence is and what history and technology it has gone through.
Next, Chapter 2 introduces the principles of AlphaGo, which impressed us with the capabilities of artificial intelligence.
From Deep Blue, which first surpassed humans in chess over 20 years ago, to AlphaGo, which defeated humans in Go and sparked a craze for artificial intelligence, we will learn about the principles.
Chapter 3 explores how autonomous driving technology works, how artificial intelligence is helping it, and why, despite this, there is still not a single fully autonomous vehicle in the field.
In Chapter 4, we will learn about the operating principles of search engines, which had a significant impact on the emergence of big data, which in turn had a significant impact on the emergence of artificial intelligence.
Once you understand how search engines took over the Internet and how they work, you'll be amazed at how Google can provide personalized search results in less than half a second.
Chapter 5 explores the secrets and inner workings of smart speakers that have transformed our daily lives.
The story unfolds in an engaging way, from how Apple's Siri pioneered a new category of artificial intelligence assistants to how the subsequent smart speakers have transformed our daily lives.
Machine translation, introduced in Chapter 6, has evolved from an era where all translation rules were determined by humans to an era where machine translation learns translation rules on its own and surpasses human translation.
The evolution of translation technology over time is philosophical and interesting.
Chapter 7 also examines the principles of chatbots, which are gaining more attention with the advent of GPT-4.
We explore what it means for humans to understand language and the principles behind how chatbots conduct human-like conversations.
Chapter 8 also examines the principles of navigation, which is a key element of the autonomous driving era and has a promising future.
Chapter 9 examines the principles of recommendation algorithms on platforms like YouTube, Netflix, Amazon, and Facebook, analyzing how they offer customers unexpected discoveries.
The explanation of the recommendation algorithm, famously known as the meme “Today, the mysterious YouTube algorithm brought me to this video”, is also interesting.
Once you understand the working principles of the artificial intelligence technologies that have become ingrained in our lives, you will experience the amazing experience of seeing your familiar daily life in a new and three-dimensional way, and your understanding will change.
AI classes as a liberal arts course for survival in the digital age
'I wake up in the morning and ask my smart speaker about the weather.
If I have any questions, I immediately search the portal.
When you go somewhere, you enter the destination into the navigation system.
'I browse through the videos recommended by YouTube or Netflix.' This is a scene from our daily lives.
And all of these scenes are made with AI technology.
As autonomous driving, search engines, smart speakers, machine translation, chatbots, navigation, and recommendation algorithms become part of our daily lives, we may feel that our lives have become more convenient, but innovative AI technologies are at work within them.
This book explains these techniques in language we can understand.
It provides a friendly explanation of the principles of artificial intelligence technology closely related to our daily lives, such as how Google finds the information we need in less than a second, how chatbots provide the right answers, and how recommendation algorithms discover our tastes.
"AI Knowledge Even Non-Majors Can Understand" was written to help diverse people understand AI and utilize it in their fields in this era where AI is a given tool.
This book explains the history and principles of AI technology in a general-level manner, making it easy for those who have never studied the subject before or find science and math difficult to understand.
The author says that AI technology will soon be used in everyday life.
Just as smartphones, which were initially used only by a select group of people, are now used by 95% of adults in our country in less than 10 years.
The author says that sooner or later, only those who know how to integrate and utilize AI in their work—from agriculture and fisheries to office work like accounting and marketing, and even specialized fields like medicine and law—will be able to keep up with the demands of the times.
The ability to leverage AI technology to find solutions at incredible speed from massive amounts of data is itself a competitive edge in business.
The author is an expert in AI technology, having created a chatbot at Kakao, a search engine at Daum, and served as the leader of the AI team at Hyundai Motor Company.
Based on these experiences, the author tells us the most useful story about AI, one that is changing the real world, rather than an abstract story surrounding it.
Additionally, over 300 pictures are provided to aid understanding instead of difficult formulas.
Jin-ho Jeong, a former developer turned IT professional illustrator, explains AI principles in simple drawings that anyone can easily understand.
Even now, AI technology is active in invisible places in our daily lives.
And these uses will only grow.
So what we need now is not fear of AI, but to realize and understand its usefulness.
This book will open new opportunities for those considering how to incorporate AI into their fields of study and work.
From ChatGPT to Google Search, Naver Papago, and YouTube algorithms.
Easily unravel the principles of all the AI technologies that have transformed our daily lives.
Before examining the full utility of artificial intelligence, this book first examines what artificial intelligence is and what history and technology it has gone through.
Next, Chapter 2 introduces the principles of AlphaGo, which impressed us with the capabilities of artificial intelligence.
From Deep Blue, which first surpassed humans in chess over 20 years ago, to AlphaGo, which defeated humans in Go and sparked a craze for artificial intelligence, we will learn about the principles.
Chapter 3 explores how autonomous driving technology works, how artificial intelligence is helping it, and why, despite this, there is still not a single fully autonomous vehicle in the field.
In Chapter 4, we will learn about the operating principles of search engines, which had a significant impact on the emergence of big data, which in turn had a significant impact on the emergence of artificial intelligence.
Once you understand how search engines took over the Internet and how they work, you'll be amazed at how Google can provide personalized search results in less than half a second.
Chapter 5 explores the secrets and inner workings of smart speakers that have transformed our daily lives.
The story unfolds in an engaging way, from how Apple's Siri pioneered a new category of artificial intelligence assistants to how the subsequent smart speakers have transformed our daily lives.
Machine translation, introduced in Chapter 6, has evolved from an era where all translation rules were determined by humans to an era where machine translation learns translation rules on its own and surpasses human translation.
The evolution of translation technology over time is philosophical and interesting.
Chapter 7 also examines the principles of chatbots, which are gaining more attention with the advent of GPT-4.
We explore what it means for humans to understand language and the principles behind how chatbots conduct human-like conversations.
Chapter 8 also examines the principles of navigation, which is a key element of the autonomous driving era and has a promising future.
Chapter 9 examines the principles of recommendation algorithms on platforms like YouTube, Netflix, Amazon, and Facebook, analyzing how they offer customers unexpected discoveries.
The explanation of the recommendation algorithm, famously known as the meme “Today, the mysterious YouTube algorithm brought me to this video”, is also interesting.
Once you understand the working principles of the artificial intelligence technologies that have become ingrained in our lives, you will experience the amazing experience of seeing your familiar daily life in a new and three-dimensional way, and your understanding will change.
GOODS SPECIFICS
- Date of issue: October 22, 2024
- Page count, weight, size: 464 pages | 660g | 145*220*30mm
- ISBN13: 9791162543931
- ISBN10: 1162543930
You may also like
카테고리
korean


korean


![ELLE 엘르 스페셜 에디션 A형 : 12월 [2025]](http://librairie.coreenne.fr/cdn/shop/files/b8e27a3de6c9538896439686c6b0e8fb.jpg?v=1766436872&width=3840)























