
Do it! Practical Machine Learning for Data Scientists
 |
Description
Book Introduction
Contains the secrets to improving the skills of a data analyst with 10 years of experience!
By implementing 13 core machine learning models directly
A book that guides machine learning beginners into the world of practice.
This book was written by the author to share with prospective practitioners the secrets to improving their skills, which he learned while working as a data analyst for 10 years.
The secret is to go back to basics and focus on studying 13 core machine learning models, including linear models and tree models.
First, we will look at the algorithmic foundations and mathematical theory underlying each model, and then implement the model directly in a simple form.
We then remodel it with an optimized Python package and compare the differences between the two to explore how machine learning works.
Machine learning is a field that beginners who have only studied theory face great difficulties when they first encounter practical applications.
The difficulties encountered at this time can ultimately be fundamentally overcome only through building up skills.
The more you understand the basic model, the more you will realize that the various models are not isolated from each other and share much theoretical commonality with the basic model.
Then, we will be able to perform machine learning modeling in actual work or research more flexibly and efficiently than before.
By implementing 13 core machine learning models directly
A book that guides machine learning beginners into the world of practice.
This book was written by the author to share with prospective practitioners the secrets to improving their skills, which he learned while working as a data analyst for 10 years.
The secret is to go back to basics and focus on studying 13 core machine learning models, including linear models and tree models.
First, we will look at the algorithmic foundations and mathematical theory underlying each model, and then implement the model directly in a simple form.
We then remodel it with an optimized Python package and compare the differences between the two to explore how machine learning works.
Machine learning is a field that beginners who have only studied theory face great difficulties when they first encounter practical applications.
The difficulties encountered at this time can ultimately be fundamentally overcome only through building up skills.
The more you understand the basic model, the more you will realize that the various models are not isolated from each other and share much theoretical commonality with the basic model.
Then, we will be able to perform machine learning modeling in actual work or research more flexibly and efficiently than before.
- You can preview some of the book's contents.
Preview
index
Preparing for Machine Learning in the First Yard
Chapter 1: Machine Learning and Python
__1.1 Understanding Machine Learning
____1.1.1 Why did machine learning emerge?
____1.1.2 A Glance at the Machine Learning Models Learned in This Book
____1.1.3 Overview of this book's learning structure
__1.2 Understanding the concepts of algorithms used in machine learning
__1.3 Setting up the practice environment
____1.3.1 Reviewing the Python Packages Used in This Book
__1.4 Quickly Experience Machine Learning Procedures
____1.4.1 Preparing the Dataset
____1.4.2 Splitting the Dataset
____1.4.3 Data Preprocessing
____1.4.4 Model Training Using Training Data
____1.4.5 Hyperparameter Tuning Using Training and Validation Data Pairs
____1.4.6 Final performance measurement and evaluation on the test dataset
Supervised learning using the second yard linear model
__Preparing a linear model
Chapter 2 Least Squares Model
__2.1 What is a least squares model?
____2.1.1 Definition of the least squares model
__2.2 Implementing the least squares model with normal equations
____2.2.1 Solution theory using normal equations
____2.2.2 Implementing the solution using normal equations
____2.2.3 Disadvantages of implementing normal equations
__2.3 Implementing a least squares model using singular value decomposition
____2.3.1 Solution theory using SVD-OLS
____2.3.2 Disadvantages of normal equation solution and advantages of SVD-OLS solution
____2.3.3 Implementing the solution using SVD-OLS
__2.4 Implementing a model using TSVD-OLS
____2.4.1 Solution theory using TSVD-OLS
____2.4.2 Implementing the solution using TSVD-OLS
Expressing as a __2.5 package
__2.6 Supplementary Lesson on Least Squares Models
____2.6.1 OLS as a statistical model
____2.6.2 Coefficient of Determination
____2.6.3 White Box Model and Black Box Model
__Reflection problem
Chapter 3 Logistic Regression Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__3.1 What is a logistic regression model?
__3.2 Implementing a Logistic Regression Model
____3.2.1 Basic theory of logistic regression model
____3.2.2 Advanced Theory of Logistic Regression Models
____3.2.3 Implementing a Logistic Regression Model
Expressing with __3.3 package
__3.4 Logistic Regression Model Supplementary Lesson
____3.4.1 Feature Scaling and Pipeline
____3.4.2 Logistic Regression Techniques as a Statistical Model
____3.4.3 Cross-validation method
____3.4.4 Feature Selection Method
__Reflection problem
Chapter 4 Lasso Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__4.1 What is a Lasso model?
__4.2 Implementing the Lasso Model
____4.2.1 Theory of Lasso Model
____4.2.2 Implementing the Lasso Model
__4.3 Expressing as a package
__4.4 Lasso Model Supplementary Lesson
____4.4.1 LARS-based Lasso model
____4.4.2 Model Selection Method
__Reflection problem
Chapter 5 Ridge Regression Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__5.1 What is a Ridge Regression Model?
__5.2 Implementing the Ridge Regression Model
____5.2.1 Basic theory of ridge regression model
____5.2.2 Advanced Theory of Ridge Regression Models
____5.2.3 Implementing the Ridge Regression Model
__5.3 Expressing as a package
__5.4 Ridge Regression Model Supplementary Lesson
____5.4.1 Bias-Variance Tradeoff and Variance in Ridge Regression
____5.4.2 Ridge Classification Model
____5.4.3 Elastic Net Regression Model
__Reflection problem
Supervised learning using the third yard tree model
__Preparing the tree model
Chapter 6 Decision Tree Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__6.1 What is a decision tree model?
__6.2 Implementing a Decision Tree Model
____6.2.1 Theory of Decision Tree Classification Models
____6.2.2 Implementing a Decision Tree Classification Model
__6.3 Expressing as a package
__6.4 Decision Tree Model Supplementary Lesson
____6.4.1 Regression Trees
____6.4.2 Grid Search
____6.4.3 Feature Importance
__Reflection problem
Chapter 7 Random Forest Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__7.1 What is a random forest model?
__7.2 Implementing a Random Forest Model
____7.2.1 Theory of Random Forest Models
____7.2.2 Implementing a Random Forest Classification Model
__7.3 Expressing as a package
__7.4 Random Forest Model Supplementary Lesson
____7.4.1 Random Forest Regression Model
____7.4.2 OOB Score
____7.4.3 ExtraTrees
____7.4.4 Feature Importance
__Reflection problem
Chapter 8: Gradient Boosting Tree Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__8.1 What is a gradient boosting tree model?
__8.2 Implementing a Gradient Boosting Tree Model
____8.2.1 Theory of Gradient Boosting Tree Model
____8.2.2 Implementing a Boosting Tree Regression Model
__8.3 Expressing as a package
__8.4 Gradient Boosting Tree Model Supplementary Lesson
____8.4.1 Explainable Artificial Intelligence
____8.4.2 Boosting techniques after the GBT model
__Reflection problem
Fourth Yard Other Map Learning Models
Chapter 9 K-Nearest Neighbor Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__9.1 What is the K-Nearest Neighbor Model?
__9.2 Implementing the K-Nearest Neighbor Model
____9.2.1 Basic theory of the KNN model
____9.2.2 Advanced Theory of KNN Model
____9.2.3 Implementing the KNN Classification Model
__9.3 Expressing as a package
__9.4 K-Nearest Neighbor Model Supplementary Lesson
____9.4.1 KNN Regression Model
____9.4.2 Decision Boundary
____9.4.3 Fixed-radius nearest neighbor model
____9.4.4 KNN Outlier Model
__Reflection problem
Chapter 10: Support Vector Machine Models
__10.1 What is a Support Vector Machine Model?
__10.2 Implementing a Support Vector Machine Model
____10.2.1 Theory of Support Vector Machine Models
____10.2.2 Implementing the SVM Model
__10.3 Expressing as a package
____10.3.1 Implementing with other packages
__10.4 Support Vector Machine Model Supplementary Lesson
____10.4.1 Extending to Support Vector Regression
____10.4.2 Probability judgment method for class classification
__Reflection problem
Chapter 11: Multilayer Perceptron Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__11.1 What is a multilayer perceptron model?
__11.2 Implementing a multilayer perceptron model
____11.2.1 Theory of the multilayer perceptron model
____11.2.2 Implementing a Multilayer Perceptron Model
__11.3 Expressing as a package
__11.4 Supplementary Lesson on Multilayer Perceptron Model
____11.4.1 MLP Regression Model
__Reflection problem
Fifth Yard Unsupervised Learning Model
Chapter 12 K-Means Clustering Model
__12.1 What is the K-Means Clustering Model?
__12.2 Implementing the K-Means Clustering Model
____12.2.1 Theory of K-Means Clustering Model
____12.2.2 Implementing the K-Means Clustering Model
__12.3 Expressing as a package
__12.4 K-Means Clustering Model Supplementary Lesson
____12.4.1 Datasets for which the K-means clustering model is not suitable
____12.4.2 Evaluating Clustering Results
__Reflection problem
Chapter 13: Hierarchical Clustering Models
__13.1 What is a hierarchical clustering model?
__13.2 Implementing a Hierarchical Clustering Model
____13.2.1 Theory of Hierarchical Clustering Models
____13.2.2 Implementing a Hierarchical Clustering Model
__13.3 Expressing as a package
__13.4 Supplementary Lesson on Hierarchical Clustering Models
____13.4.1 Visualizing Cluster Hierarchies with Dendrograms
__Reflection problem
Chapter 14 Principal Component Analysis Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__14.1 What is a principal component analysis model?
__14.2 Implementing a principal component analysis model
____14.2.1 Theory of Principal Component Analysis Model
____14.2.2 Implementing the PCA Model
__14.3 Expressing as a package
__14.4 Principal Component Analysis Model Supplementary Lesson
____14.4.1 Various dimensionality reduction techniques
__Reflection problem
[Appendix] Machine Learning Terminology at a Glance
Solving the reflection problem
References
Search
Chapter 1: Machine Learning and Python
__1.1 Understanding Machine Learning
____1.1.1 Why did machine learning emerge?
____1.1.2 A Glance at the Machine Learning Models Learned in This Book
____1.1.3 Overview of this book's learning structure
__1.2 Understanding the concepts of algorithms used in machine learning
__1.3 Setting up the practice environment
____1.3.1 Reviewing the Python Packages Used in This Book
__1.4 Quickly Experience Machine Learning Procedures
____1.4.1 Preparing the Dataset
____1.4.2 Splitting the Dataset
____1.4.3 Data Preprocessing
____1.4.4 Model Training Using Training Data
____1.4.5 Hyperparameter Tuning Using Training and Validation Data Pairs
____1.4.6 Final performance measurement and evaluation on the test dataset
Supervised learning using the second yard linear model
__Preparing a linear model
Chapter 2 Least Squares Model
__2.1 What is a least squares model?
____2.1.1 Definition of the least squares model
__2.2 Implementing the least squares model with normal equations
____2.2.1 Solution theory using normal equations
____2.2.2 Implementing the solution using normal equations
____2.2.3 Disadvantages of implementing normal equations
__2.3 Implementing a least squares model using singular value decomposition
____2.3.1 Solution theory using SVD-OLS
____2.3.2 Disadvantages of normal equation solution and advantages of SVD-OLS solution
____2.3.3 Implementing the solution using SVD-OLS
__2.4 Implementing a model using TSVD-OLS
____2.4.1 Solution theory using TSVD-OLS
____2.4.2 Implementing the solution using TSVD-OLS
Expressing as a __2.5 package
__2.6 Supplementary Lesson on Least Squares Models
____2.6.1 OLS as a statistical model
____2.6.2 Coefficient of Determination
____2.6.3 White Box Model and Black Box Model
__Reflection problem
Chapter 3 Logistic Regression Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__3.1 What is a logistic regression model?
__3.2 Implementing a Logistic Regression Model
____3.2.1 Basic theory of logistic regression model
____3.2.2 Advanced Theory of Logistic Regression Models
____3.2.3 Implementing a Logistic Regression Model
Expressing with __3.3 package
__3.4 Logistic Regression Model Supplementary Lesson
____3.4.1 Feature Scaling and Pipeline
____3.4.2 Logistic Regression Techniques as a Statistical Model
____3.4.3 Cross-validation method
____3.4.4 Feature Selection Method
__Reflection problem
Chapter 4 Lasso Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__4.1 What is a Lasso model?
__4.2 Implementing the Lasso Model
____4.2.1 Theory of Lasso Model
____4.2.2 Implementing the Lasso Model
__4.3 Expressing as a package
__4.4 Lasso Model Supplementary Lesson
____4.4.1 LARS-based Lasso model
____4.4.2 Model Selection Method
__Reflection problem
Chapter 5 Ridge Regression Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__5.1 What is a Ridge Regression Model?
__5.2 Implementing the Ridge Regression Model
____5.2.1 Basic theory of ridge regression model
____5.2.2 Advanced Theory of Ridge Regression Models
____5.2.3 Implementing the Ridge Regression Model
__5.3 Expressing as a package
__5.4 Ridge Regression Model Supplementary Lesson
____5.4.1 Bias-Variance Tradeoff and Variance in Ridge Regression
____5.4.2 Ridge Classification Model
____5.4.3 Elastic Net Regression Model
__Reflection problem
Supervised learning using the third yard tree model
__Preparing the tree model
Chapter 6 Decision Tree Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__6.1 What is a decision tree model?
__6.2 Implementing a Decision Tree Model
____6.2.1 Theory of Decision Tree Classification Models
____6.2.2 Implementing a Decision Tree Classification Model
__6.3 Expressing as a package
__6.4 Decision Tree Model Supplementary Lesson
____6.4.1 Regression Trees
____6.4.2 Grid Search
____6.4.3 Feature Importance
__Reflection problem
Chapter 7 Random Forest Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__7.1 What is a random forest model?
__7.2 Implementing a Random Forest Model
____7.2.1 Theory of Random Forest Models
____7.2.2 Implementing a Random Forest Classification Model
__7.3 Expressing as a package
__7.4 Random Forest Model Supplementary Lesson
____7.4.1 Random Forest Regression Model
____7.4.2 OOB Score
____7.4.3 ExtraTrees
____7.4.4 Feature Importance
__Reflection problem
Chapter 8: Gradient Boosting Tree Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__8.1 What is a gradient boosting tree model?
__8.2 Implementing a Gradient Boosting Tree Model
____8.2.1 Theory of Gradient Boosting Tree Model
____8.2.2 Implementing a Boosting Tree Regression Model
__8.3 Expressing as a package
__8.4 Gradient Boosting Tree Model Supplementary Lesson
____8.4.1 Explainable Artificial Intelligence
____8.4.2 Boosting techniques after the GBT model
__Reflection problem
Fourth Yard Other Map Learning Models
Chapter 9 K-Nearest Neighbor Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__9.1 What is the K-Nearest Neighbor Model?
__9.2 Implementing the K-Nearest Neighbor Model
____9.2.1 Basic theory of the KNN model
____9.2.2 Advanced Theory of KNN Model
____9.2.3 Implementing the KNN Classification Model
__9.3 Expressing as a package
__9.4 K-Nearest Neighbor Model Supplementary Lesson
____9.4.1 KNN Regression Model
____9.4.2 Decision Boundary
____9.4.3 Fixed-radius nearest neighbor model
____9.4.4 KNN Outlier Model
__Reflection problem
Chapter 10: Support Vector Machine Models
__10.1 What is a Support Vector Machine Model?
__10.2 Implementing a Support Vector Machine Model
____10.2.1 Theory of Support Vector Machine Models
____10.2.2 Implementing the SVM Model
__10.3 Expressing as a package
____10.3.1 Implementing with other packages
__10.4 Support Vector Machine Model Supplementary Lesson
____10.4.1 Extending to Support Vector Regression
____10.4.2 Probability judgment method for class classification
__Reflection problem
Chapter 11: Multilayer Perceptron Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__11.1 What is a multilayer perceptron model?
__11.2 Implementing a multilayer perceptron model
____11.2.1 Theory of the multilayer perceptron model
____11.2.2 Implementing a Multilayer Perceptron Model
__11.3 Expressing as a package
__11.4 Supplementary Lesson on Multilayer Perceptron Model
____11.4.1 MLP Regression Model
__Reflection problem
Fifth Yard Unsupervised Learning Model
Chapter 12 K-Means Clustering Model
__12.1 What is the K-Means Clustering Model?
__12.2 Implementing the K-Means Clustering Model
____12.2.1 Theory of K-Means Clustering Model
____12.2.2 Implementing the K-Means Clustering Model
__12.3 Expressing as a package
__12.4 K-Means Clustering Model Supplementary Lesson
____12.4.1 Datasets for which the K-means clustering model is not suitable
____12.4.2 Evaluating Clustering Results
__Reflection problem
Chapter 13: Hierarchical Clustering Models
__13.1 What is a hierarchical clustering model?
__13.2 Implementing a Hierarchical Clustering Model
____13.2.1 Theory of Hierarchical Clustering Models
____13.2.2 Implementing a Hierarchical Clustering Model
__13.3 Expressing as a package
__13.4 Supplementary Lesson on Hierarchical Clustering Models
____13.4.1 Visualizing Cluster Hierarchies with Dendrograms
__Reflection problem
Chapter 14 Principal Component Analysis Model
__Preliminary knowledge review
__14.1 What is a principal component analysis model?
__14.2 Implementing a principal component analysis model
____14.2.1 Theory of Principal Component Analysis Model
____14.2.2 Implementing the PCA Model
__14.3 Expressing as a package
__14.4 Principal Component Analysis Model Supplementary Lesson
____14.4.1 Various dimensionality reduction techniques
__Reflection problem
[Appendix] Machine Learning Terminology at a Glance
Solving the reflection problem
References
Search
Detailed image
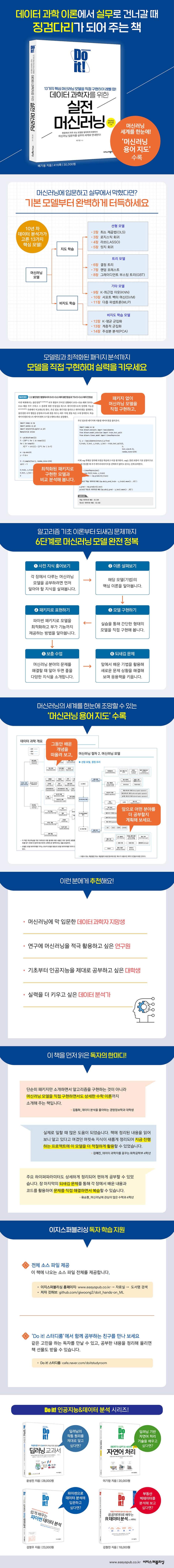
Publisher's Review
Are you new to machine learning and stuck in practice?
When developing the skills needed for practical work!
Machine learning is a field where the gap between beginner and practical knowledge is very wide.
The package usage instructions and practice codes in the introductory book are not easy to apply to actual research or work environments, and even if you try to find and use codes through Google depending on the situation, they often become useless the moment the environment or conditions change even slightly.
The author of this book also faced similar problems when he first started studying machine learning.
Having wrestled with machine learning in the field for over a decade, I've realized that to truly develop your skills, you need to focus on mastering the theory and usage of the core models that underpin all machine learning techniques.
This book is for those like the author who have just started learning machine learning and are struggling in practice. It may seem a bit difficult, but it will show you the fastest way to improve your skills and the shortcut to success.
By implementing the 13 core models directly,
Develop practical application skills that can be applied immediately to real work.
So how can we fully understand the underlying models? This book introduces 13 core machine learning models and suggests ways to implement them in simple forms.
The experience of simply creating diverse and complex models and solving problems may not be fully embodied in my current skills.
Also, in real life, the given environment is always going to change, so you need to know how to change the shape of the model to your liking.
The more you delve into the theory and usage of the major basic models, the easier it will be to understand other models. Furthermore, you will realize that most core parts of any machine learning model theoretically share the same basic model.
Learning this way will help you become more flexible and reduce unnecessary attempts when performing machine learning modeling in actual work or research.
From algorithm theory to hyperparameter analysis
A thorough exploration of machine learning from start to finish.
In this book, we will learn machine learning in the following order.
First, we will review the fundamental algorithmic theory underlying each machine learning model and gain a deeper understanding of its operating principles along with mathematical theory.
And let's implement the model by directly coding it in a simple form.
Next, we model using the Python package optimized for the model built into scikit-learn, compare it with the model we created ourselves, and explore the differences.
Finally, we will look at the hyperparameters used in the Python package to understand the package's operation in more detail.
If you're new to machine learning or have been studying it for a while, you can review the "Preliminary Knowledge Overview" to get a preview of the knowledge needed to understand the models covered in each chapter.
Additionally, at the end of each chapter, we introduce 'Supplementary Lessons' that provide valuable knowledge for those who wish to become machine learning experts.
A bird's eye view of the world of machine learning
Includes a 'Machine Learning Terminology Map'!
A 'terminology map' is provided as an appendix to help you understand the various fields, types, and concepts of machine learning at a glance.
Let's explore this map to see how the world of machine learning is structured and what we've learned from this book.
Let's have fun thinking about where to explore machine learning in the future.
Come to the 'Do it! Study Room' where we learn, share, and grow together!
If you plan and study alone, you will quickly become tired.
Let's meet readers who have similar concerns and share difficult content.
Studying while helping each other is more rewarding.
If you want to go far, go with a friend.
- Do it! Study Room: cafe.naver.com/doitstudyroom
Example source files are available on the Aegis Publishing website's data room or the author's GitHub.
- Easy Publishing website: www.easyspub.co.kr → Click [Data Room] → Search for book title
- Author's GitHub: github.com/giwoong2/doit_hands-on_ML
When developing the skills needed for practical work!
Machine learning is a field where the gap between beginner and practical knowledge is very wide.
The package usage instructions and practice codes in the introductory book are not easy to apply to actual research or work environments, and even if you try to find and use codes through Google depending on the situation, they often become useless the moment the environment or conditions change even slightly.
The author of this book also faced similar problems when he first started studying machine learning.
Having wrestled with machine learning in the field for over a decade, I've realized that to truly develop your skills, you need to focus on mastering the theory and usage of the core models that underpin all machine learning techniques.
This book is for those like the author who have just started learning machine learning and are struggling in practice. It may seem a bit difficult, but it will show you the fastest way to improve your skills and the shortcut to success.
By implementing the 13 core models directly,
Develop practical application skills that can be applied immediately to real work.
So how can we fully understand the underlying models? This book introduces 13 core machine learning models and suggests ways to implement them in simple forms.
The experience of simply creating diverse and complex models and solving problems may not be fully embodied in my current skills.
Also, in real life, the given environment is always going to change, so you need to know how to change the shape of the model to your liking.
The more you delve into the theory and usage of the major basic models, the easier it will be to understand other models. Furthermore, you will realize that most core parts of any machine learning model theoretically share the same basic model.
Learning this way will help you become more flexible and reduce unnecessary attempts when performing machine learning modeling in actual work or research.
From algorithm theory to hyperparameter analysis
A thorough exploration of machine learning from start to finish.
In this book, we will learn machine learning in the following order.
First, we will review the fundamental algorithmic theory underlying each machine learning model and gain a deeper understanding of its operating principles along with mathematical theory.
And let's implement the model by directly coding it in a simple form.
Next, we model using the Python package optimized for the model built into scikit-learn, compare it with the model we created ourselves, and explore the differences.
Finally, we will look at the hyperparameters used in the Python package to understand the package's operation in more detail.
If you're new to machine learning or have been studying it for a while, you can review the "Preliminary Knowledge Overview" to get a preview of the knowledge needed to understand the models covered in each chapter.
Additionally, at the end of each chapter, we introduce 'Supplementary Lessons' that provide valuable knowledge for those who wish to become machine learning experts.
A bird's eye view of the world of machine learning
Includes a 'Machine Learning Terminology Map'!
A 'terminology map' is provided as an appendix to help you understand the various fields, types, and concepts of machine learning at a glance.
Let's explore this map to see how the world of machine learning is structured and what we've learned from this book.
Let's have fun thinking about where to explore machine learning in the future.
Come to the 'Do it! Study Room' where we learn, share, and grow together!
If you plan and study alone, you will quickly become tired.
Let's meet readers who have similar concerns and share difficult content.
Studying while helping each other is more rewarding.
If you want to go far, go with a friend.
- Do it! Study Room: cafe.naver.com/doitstudyroom
Example source files are available on the Aegis Publishing website's data room or the author's GitHub.
- Easy Publishing website: www.easyspub.co.kr → Click [Data Room] → Search for book title
- Author's GitHub: github.com/giwoong2/doit_hands-on_ML
GOODS SPECIFICS
- Date of issue: August 14, 2023
- Page count, weight, size: 416 pages | 870g | 188*257*16mm
- ISBN13: 9791163034964
You may also like
카테고리
korean


korean


![ELLE 엘르 A형 (여성월간) : 1월 [2026]](http://librairie.coreenne.fr/cdn/shop/files/3b70e1cf77cf67d6da56e0eb041901e8.jpg?v=1767265322&width=3840)























